As the web and its users evolve, so does search engine optimization. It’s important that your website be discoverable by search engines, but it can be challenging to stay up to date with relevant best practices. Learn about the state of SEO today and follow our checklist for increasing organic traffic to your site by making the most of Drupal’s core features and SEO modules.
What is SEO?
Search engine optimization, or SEO, is the practice of optimizing your web content to improve discoverability by search engines—and therefore, your audiences. In the early days of SEO, this usually meant creating a keyword strategy for search queries and building content around those keywords—often using keywords several times in titles, headings and image alt text. This practice, called keyword stuffing, has thankfully declined in popularity due to improved algorithms created by search engines like Google that can detect these gimmick-y tactics and postulate the semantic meaning of website content to match users with the most relevant results. These days, search engine optimization is about high quality content and a technically sound, user-friendly website.
Why an SEO strategy (still) matters for your Drupal website
Unfortunately, even after adding unique and compelling content, you may find that your web pages don’t show up on the first page of results. This can be a real blow to your website traffic because research conducted as recently as June 2021 shows that organic search drives nearly half of all traffic to websites—and significantly more if you count local search (e.g., “Pizza restaurants near me” or “Pizza in Portland, Maine”). So if you want to be discoverable to this large source of potential customers and even current users, you need to make sure your content is showing up for relevant search queries.
While search engines have come a long way, they aren’t magical. They still rely on algorithms and data points to determine what constitutes high quality content and a technically sound, user-friendly site. And perhaps most importantly, they don’t know your users as well as you do. By understanding the way search engines like Google work and ensuring your website provides relevant content in the most understandable and accessible ways for your users, you can greatly increase your chances of being discovered in search engines.
An SEO strategy for Drupal
If you’re using a content management system like Drupal, you’ve already laid the foundation for a solid SEO strategy. And if you’ve upgraded to Drupal 9, you’ve got access to easy and flexible content authoring, which is the backbone of a good content strategy, as well as Drupal’s latest features. (And if you haven’t upgraded to Drupal 9 yet, get in touch!)
However, you can do a lot more to make your Drupal website easier for your users and search engines to understand and access. A Drupal SEO strategy should involve technical optimization, thoughtful information architecture, and a robust content strategy. Our Drupal SEO checklist walks you through the most important considerations in each category and makes Drupal-specific recommendations for how to use core modules and which contributed modules to add to your toolkit.
Drupal SEO Strategy Checklist
Technical performance
Responsiveness (optimize for every device): Google uses a mobile-first indexing approach, which means that the mobile version of your content is crawled, indexed, and ranked by Google’s bots. So, even if you don’t think your audience is inclined to use mobile, it’s important that your website is responsive and that your content is well structured on all sizes of mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and desktop computers.
What you should do: With Drupal 9, a basic level of responsiveness is built in. However, this doesn’t mean that the mobile design will look or respond how you imagine it should. Take a look at your website on various screen sizes and devices and ensure that it is 100% viewable and functional for mobile users and that content and features appear in the order you expect. Going forward, take a mobile-first approach to visual and user-experience design.
Page speed: Users expect web content to load almost instantaneously. Recognizing this demand, Google uses a ranking factor called Core Web Vitals to determine how quickly users can access your content. It evaluates things like how long it takes the largest element on your page to load, how much layout shift occurs on a page while it’s loading, and how long it takes for elements on a page to respond to user inputs (e.g., clicks). Your website’s Core Web Vitals directly impact your ranking within Google’s search engine results pages.
What you should do: Continuously audit your website’s performance and identify areas for improvement. You’ll want to work with skilled Drupal developers to ensure that images are compressed, your site’s code is clean, and that unnecessary code is removed. It’s also important to limit redirects and handle any necessary redirects properly. You can use a Drupal module like Redirect to manage, save, and delete redirects from the Drupal administrative interface.
Accessibility: Naturally, if your goal is to make your content discoverable, it’s important that your content is accessible to all users, which means ensuring it can be accessed and understood by users with disabilities and users facing socio-economic restrictions, such as low bandwidth. While Google doesn’t currently take specific elements of the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines into account, many of its “page experience update” metrics added to the algorithm in 2021 have a direct correlation to accessibility. Moreover, it’s likely that search engines will continue to add user experience ranking factors over time, and ensuring that your website is accessible will future-proof your website for algorithms.
What you should do: Drupal 9 has robust accessibility features built in. However, designers, developers, and content editors can introduce accessibility issues if they aren’t careful. It’s important to continually audit your website for accessibility by familiarizing yourself with website accessibility best practices and using tools like SiteImprove that assess your website and provide actionable, prioritized tasks for improving accessibility. A Drupal SiteImprove module enhances the tool for your Drupal site by allowing content editors to see these analyses right from the Drupal administrative interface.
Information architecture & user experience
Navigation: Website navigation is important for SEO because it helps search engines (and people) understand what pages are most important and how they relate to one another. Even if your site relies on a robust internal search experience, web content can be organized through various types of navigational elements such as breadcrumbs (a secondary navigation system that shows a user's location in a site).

What you should do: Ensure that your most important content is no more than 1-2 clicks away from the home page. For instance, if a user navigates from the home page to a blog post by clicking a blog link and then the title of an individual post, that’s two clicks. Then, use a Drupal module such as Easy Breadcrumb or Menu Breadcrumb to automatically generate breadcrumbs on every page of your site. Additionally, you may want to use a module like Pathauto to automatically assign structured, user-friendly URLs to your Drupal nodes.
Link management: Links are the backbone of the web. When search engines “crawl” your site, they follow links from known pages to discover additional pages. That means if your links are broken, search engines won’t be able to find or serve your pages. Broken links also mean that users won’t be able to see your content—a frustrating experience that ultimately hurts your site’s discoverability.
What you should do: For link management, use a Drupal module like Link Checker to scan your site for broken links. The module provides a report of broken links on your site and can be configured to run periodically or even to unpublish nodes after a specified number of 404 (page not found) errors. To prevent broken links from occurring in the first place, try using a module like Linkit that gives content editors an autocomplete field for linking content in a WYSIWYG editor, reducing the likelihood of mistyped or outdated URLs. You may find ahrefs.com a useful resource as well, which offers a lot of link management reports we use with all Redfin clients.
Site maps: A XML sitemap is a collection of all the important pages on your site that are meant to be crawled by search engines. It acts as a roadmap to tell search engines where to start. It’s especially beneficial for large websites and new websites that have fewer backlinks (links from external sources).
What you should do: General a sitemap using the Simple XML sitemap module. This sitemap tool supports multilingual content and covers most of Drupal’s core entity types (e.g. nodes, taxonomy terms) out of the box. It also automatically submits your sitemap to search engines.
On-page optimization
Semantic structure: The semantic structure of your content is a big deal for search engines, as well as for users. Like users, search engines rely on “clues” to determine content hierarchy, context, and relationships. However, search engines can’t rely on some of the visual clues that some users respond to. Instead, the HTML markup provides these semantic clues. For instance, an <h1> tag tells a search engine that the content contained within that tag is a top-level header and an <a> tag defines a hyperlink. Without correctly applied markup, a search engine will just “see” a bunch of text.
What you should do: Ensure that your web developers are using best practices for writing clean, accessible code. Then, make sure that content editors inserting code via WYSIWYG editors are aware that headings and other tags—often misused to convey emphasis—have important semantic meaning to users and search engines alike. Following our guide to writing accessible content in a content management system is a great place to start!
Metadata: Meta tags and descriptions are often seen as near synonymous with SEO. Meta tags are structured content descriptions that tell search engines and social networks, such as Facebook or Twitter, important information about your web page. The title tag and meta description attribute are the most commonly used by search engines.
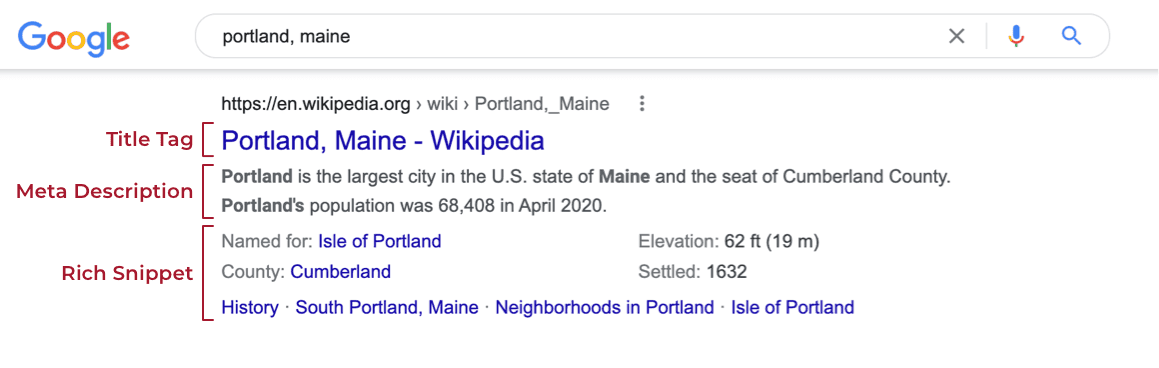
What you should do: Use the Metatag module to set tags like page title and description, as well as the image to be used when a page is shared on Twitter or Facebook. A great feature of this module is that you can set default tags for all items of a certain type. For instance, you could set the blog post title tag to always display “[Current page title] | [Site name]” (e.g. “The Drupal 9 SEO Checklist | Redfin Solutions, LLC”) and the description to pull the value of a particular field on that content type, such as a summary or subtitle field. To go beyond these basic metatags, you can also use the Schema.org Metatag module to further define structured data for your content according to Schema.org’s schemas for structured data on the Internet.
Content strategy
Know your audience (and write for them): The most important aspect of any content strategy is to know your audience—and to develop content for them based on that knowledge! If you want to show up in the search results for your target audiences, the first step is to know what it is they’re searching and why.
What you should do: Develop a plan for your content based on user research and existing personas and user journeys. After coming up with some topics, conduct some queries of your own and see what Google offers for related queries. Pay attention to what type of content your competitors are creating and how it shows up in search results. Gather data from Google Analytics about your traffic sources and mediums so you have a benchmark for determining how you’re acquiring traffic. Continue to track this over time as you hone your strategy.
Answer questions: Have you ever typed a question into the Google search box and been provided immediately with an answer before scrolling down to the full search results page or clicking a link. For example, try typing “How long does a cake take to cool?” into your search bar. If you were served a bit of text letting you know that as a general rule of thumb you should let your cake cool for 10-15 minutes, you witnessed a “featured snippet." While the jury is still out on whether featured snippets are the best search solution, Google’s latest algorithm, the Multitask Unified Model (MUM) makes it clear that Google aims to help users by answering complex questions.
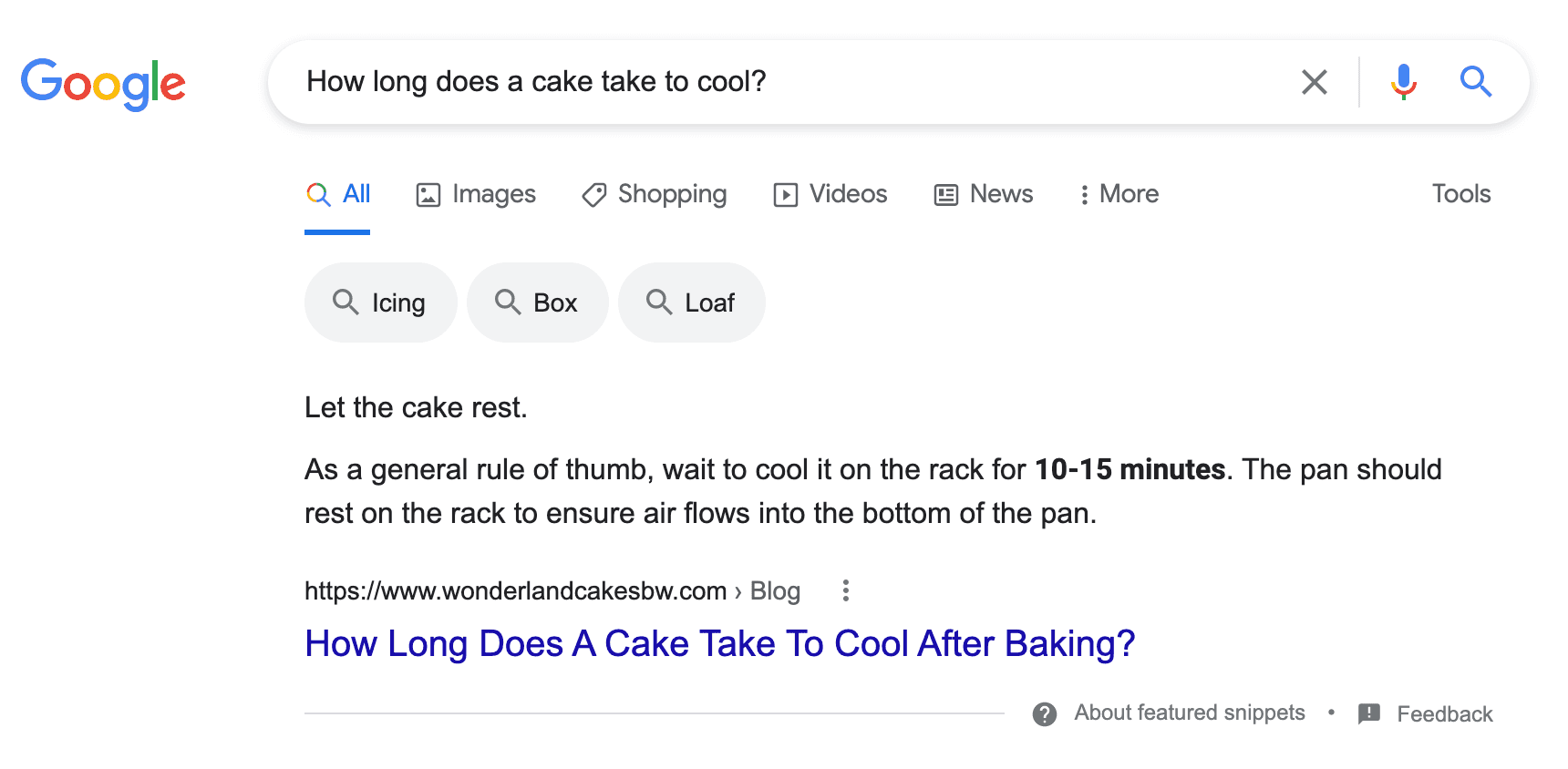
What you should do: This one dovetails with knowing and writing for your audience. Write content that directly answers your target audience’s questions. There’s no guarantee that Google will pull your content for a featured snippet. However, you’ll still be tapping into the mental model that Google has identified for how users expect to search for and find content.
(Re)fresh content: It can take time for your content to build up its authority and reputation (sometimes referred to as “link equity”) with search engines. Unless you’re a news publishing organization, your top content probably needs to gain credibility through links from other sources. Therefore, it’s important to keep your older content relevant, so you can take advantage of the equity it has built up over time.
What you should do: Make a list of last year’s top performing pages and see if there’s anything that should be updated to reflect new insights or timely changes. These don’t have to be large changes. Just keep your content fresh and remember not to change the page path (URL) if you don’t have to. If changing the page path is necessary, use the Redirect module to ensure a redirect is set up correctly.
Conclusion
In 2022, it’s more important than ever that your SEO strategy include elements like information architecture and user experience alongside general technical optimization and quality content. Thankfully, in the right hands, your Drupal website can handle it all.
If you need help devising your SEO strategy, upgrading your website to Drupal 9, or taking advantage of some of the Drupal modules outlined here, contact the Redfin Solutions team!
